Genetic studies have revolutionized our understanding of human health, providing insights into our medical histories and dispositions. By examining the DNA that we inherit from our ancestors, genetic research helps us understand how certain traits, conditions, and diseases are passed down through generations. This knowledge allows us to make more informed health decisions, improve disease prevention, and ultimately, influence the well-being of future generations.
One key aspect of genetic studies is their ability to identify predispositions to certain diseases. By analyzing a person’s genome, scientists can detect variations that increase the likelihood of developing conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or cancer. For example, mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are linked to a higher risk of breast and ovarian cancers. People with a family history of these cancers can undergo genetic testing to determine if they carry these mutations, which can then inform decisions about preventive measures, such as more frequent screenings or even preventive surgery.

In addition to identifying genetic predispositions, genetic studies help us understand how individuals may respond to specific treatments and medications—a field known as pharmacogenomics. Genetic variations can influence how a person metabolizes certain drugs, affecting the efficacy and safety of those treatments. For instance, some people carry genetic variants that make them poor metabolizers of certain medications, which can result in adverse effects or insufficient drug efficacy. With genetic information, doctors can tailor medication dosages to each patient, improving outcomes and reducing the risk of side effects.
Beyond individual health, genetic research can provide valuable information for future generations. By understanding our genetic makeup, we can make better lifestyle and health choices that reduce the risk of passing certain conditions to our offspring. For example, knowledge about genetic risks of heart disease can motivate individuals to adopt healthier diets, regular exercise, and routine checkups, potentially minimizing the genetic impact on the next generation. Furthermore, genetic counseling can guide families in making reproductive choices, helping them understand the likelihood of passing on inherited conditions to their children.
Genetic studies also provide insights into population-level health trends. By examining genetic diversity across different groups, researchers can identify why certain populations are more susceptible to specific diseases, like sickle cell anemia in African populations or cystic fibrosis among those of European descent. This helps in designing targeted public health interventions and screening programs that address specific community needs.
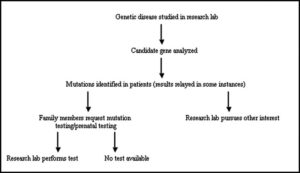
In summary, genetic studies empower individuals and families to make better health choices by revealing their predispositions, guiding personalized treatment plans, and informing preventive measures. This knowledge not only enhances individual health but also contributes to the well-being of future generations, allowing us to create a healthier legacy for our descendants.
(Please enter your Payment methods data on the settings pages.)